- Home
- For New Patients
- Our Procedures
- Carotid Artery Stenting
Carotid Artery Stenting

- Stents used for carotid artery stenting

- Cerebral protection basket
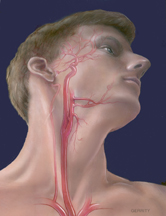
The longstanding, traditional way of fixing blockage of the carotid artery is with a surgery called endarterectomy, where a vascular surgeon cuts the artery open and removes the plaque. This is a very good surgery, with low complication rates in good hands.
However, it has recently been discovered that in patients that are at high risk for surgery, carotid stenting may have distinct advantages. These high risk factors include patients with blockage of the other carotid artery, blockage in a site that has already been opened surgically in the past (called restenosis), patients with advanced heart and lung disease, patients who have received radiation to the neck for treatment of cancer, and others. In these high risk surgical patients, carotid stenting is a better option because there is less chance of having a stroke or other complications with the stent procedure.
The stent prodecure is similar to a heart catheterization procedure. The doctor inserts a catheter through the groin, places that catheter through the blockage, and opens a filter above the blockage to catch any plaque that may break off during the procedure. The blockage is then opened with a stent. The filter is withdrawn, and the artery stays open, decreasing the chances of ever having a stroke.
- For more information, visit:
http://www.sirweb.org/patients/stroke/ or visit Abbott Vascular on the web.
